Innovation
Revolutionizing Gas Sterilization Technology
The Andersen EO-Flexible Chamber Technology (EO-FCT) represents a groundbreaking approach to gas sterilization. This method not only enhances efficiency but also ensures a gentler sterilization process at lower temperatures.

EO of Yersteryear
Hospital Sterilization
Skip to: Contract Sterilization
Ethylene oxide was extensively tested by US government labs in the 1930s and 1940s and it was recognized as a promising sterilizing agent. In the 1950s, the widespread introduction of plastics to medical devices required a low-temperature method of sterilization compatible with these new materials. EO systems were developed for hospital use, and by the 1960s, EO had become the dominant low-temperature sterilization method in US healthcare facilities.
These early hospital EO sterilizers were a breakthrough in low-temperature sterilization, but they were not without problems.
Environmental Concerns: Ethylene oxide is flammable and explosive in concentrations above 3%. Manufacturers of these tank systems reduced the potential danger by mixing EO with inert gases. The mixes, however, introduced their own problems – they were far less efficient and (unlike 100% EO) the inert gasses used were discovered to be greenhouse gasses. These EO mixture systems were scheduled for phase-out in the early 1990s and were taken off the market in 2012.
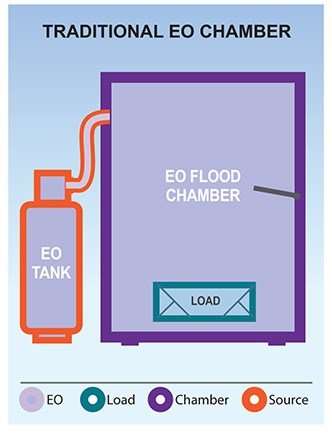
Large tanks of gas: Early hospital EO systems were typically fed by large external 50lb tanks. These systems used pounds of EO per cycle, and supplies of additional large tanks required storage in specially ventilated rooms.
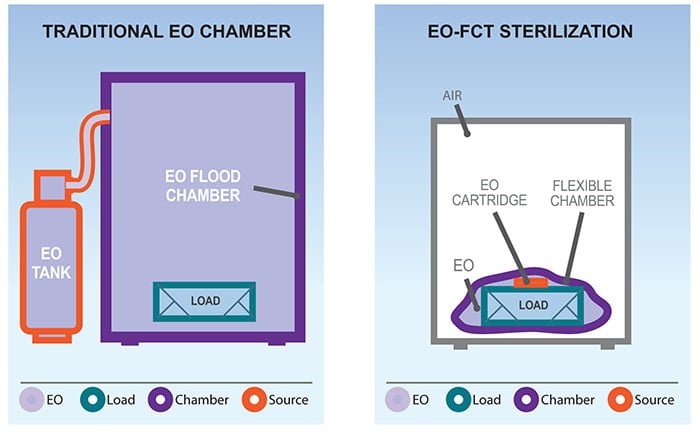
Wasted Space: Besides the storage room for EO tanks, these early systems required external air compressors and fixed water lines. EO sterilizers of this era were built into wall units with a service room behind the sterilizers. The EO sterilizers themselves were installed in separate rooms to prevent EO from entering the general workspace (see illustration). This extra room meant hospitals had to dedicate a large amount of space to the installation and operation of their EO sterilizers.

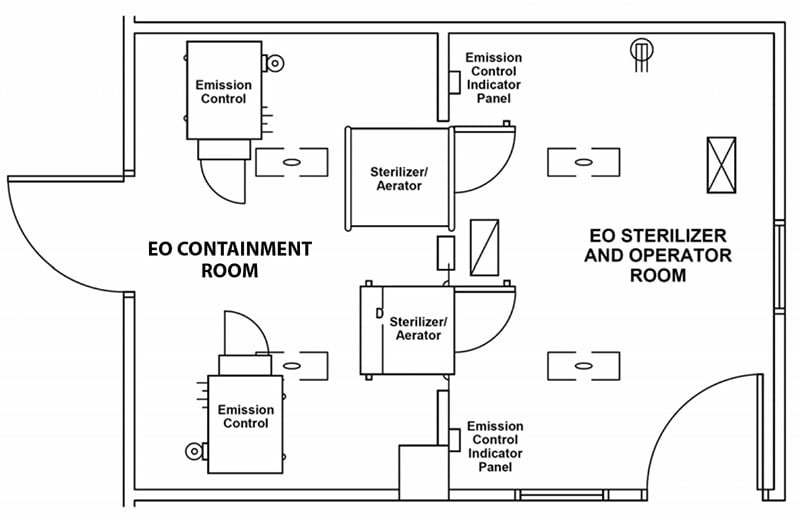
NOTE: As explained in the How EO-FCT Works section, our “chamber within a chamber” EO-FCT system performs the same function as an installation in a dedicated room as recommended by some industry guidance – making our cabinets a convenient and space-efficient option in any setting.
While EO is an extremely effective sterilant with the widest range of material compatibility, the early traditional EO chamber systems had some significant drawbacks. In the mid-1990s Hospitals began to move away from EO and toward other options such as H2O2 and PPA. We discuss how EO compares to H2O2 and PPA here.
Sterilization
Contract Sterilization
Traditional contract EO sterilization facilities sterilize medical devices by the pallet load. Many current EO “pallet chambers” have the ability to sterilize over fifty pallets of product at once. EO pallet chambers are the typical method for sterilizing most new medical devices, especially products that are produced in large quantities.
However, these large EO contract facilities may not be the best option for manufacturers of specialty devices that are produced in smaller volumes. Likewise, firms that are developing new devices and require a fast turnaround of small numbers of devices require a different solution.
Gas usage is also an issue. A typical EO contract sterilization facility uses between 6 to 8 lbs. of EO to sterilize a single pallet of devices. In contrast, our Andersen contract option with a modified EO-FCT system uses just .9 to 1.6 lbs. to process the same volume of product. That’s 77 to 87% reduction of EO consumption.
All of this seems so much more relevant when we speak in terms of the bottom line. With Andersen (in-house or contract) you are able to reduce turnaround time, better manage your inventory and maintain control over your product. Contact us to discuss if Andersen contract sterilization or in-house processing is right for you.
Please also see the Environmental Impact tab.
How it works
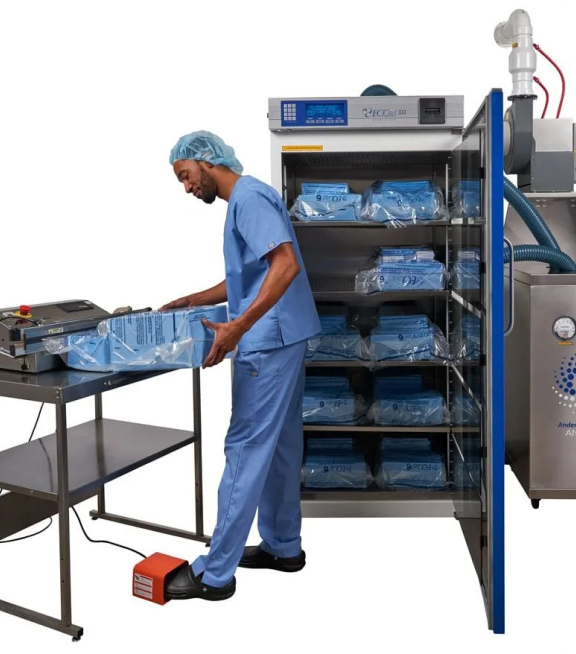
Ethylene Oxide-Flexible Chamber Technology (EO-FCT) is Andersen’s secret sauce. It is exclusive, tested and patented. We have several FDA Clearances. Our process is precise, reliable and proven.
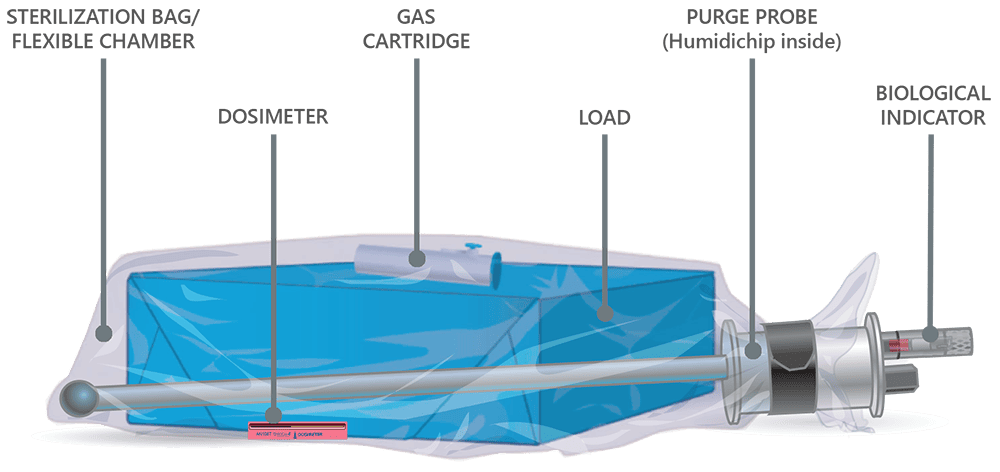
- The operator readies a load inside the sterilization bag with appropriate accessories, gathers the top of the bag around the purge probe bobbin, secures it with the blue strap, attaches the purge probe quick connect and turns on the machine.
- The purge probe pulls out all excess air.
- Operator activates ampoule/cartridge to release EO inside the sterilization bag, closes the door and starts the cycle. EO works through to the center of the load.
- Anprolene AN74, EOGas 3: EO slowly permeates through the outer sterilization bag and into the cabinet where it is actively pulled to the outside.
- Anprolene AN75, EOGas 4: The EO is held in the sterilization bag through the entire exposure cycle and then pulled out through the purge probe and exhausted to the outdoors during the aeration process.
- Every two minutes, air is pumped into the bag and pulled back out, much like a lung, throughout aeration. Active aeration continues until an operator removes the load, even after the selected aeration cycle ends.
So that’s how EO-FCT works, in a nutshell. A rather apt metaphor. Like a nut, Andersen’s EO-FCT is so effective because it acts as a “chamber within a chamber.”
Hospital Sterilization Revolutionized by EO-FCT
To look at it from a classic hospital EO sterilization angle (see EO of Yesteryear tab), the sterilization bag acts as the EO containment room while the cabinet acts as the operator room. The function of the containment room was to protect operators from incidental exposure – by, ah-hem, containing EO to the one room that was rarely accessed. Our sterilization bag is like the containment room. Our cabinet is like the operator’s room, providing an extra level of protection between the operator and EO. More than just extra space, the cabinet uses negative pressure to consistently keep air moving from the front to the back and then to the outside—much like a ventilation hood.
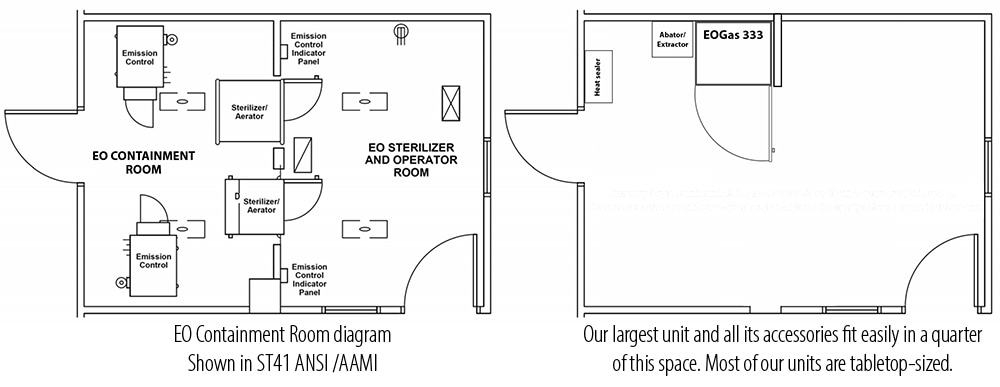
Contract Sterilization Revolutionized by EO-FCT
Similar to a classic contract sterilization angle, our sterilization bag performs the same function as a huge rigid sterilization chamber without the exhaust. Classic contract sterilization doesn’t have the equivalent of the exterior chamber because excess EO is burned off or exhausted into the environment.
Terminal Sterility
Achieves FDA-required 10-6 sterility assurance level (SAL) for terminal sterilization of medical devices.
Easy Installation
Easiest in the industry; requires only a dedicated electrical outlet and an exhaust line. See your sterilizer’s specific specs for full details.
Micro-dose
Terminal sterility (10-6 SAL) with 90% less EO than any other system on the market. EOGas 3 sterilizers use even less per cycle.
Zero Emissions
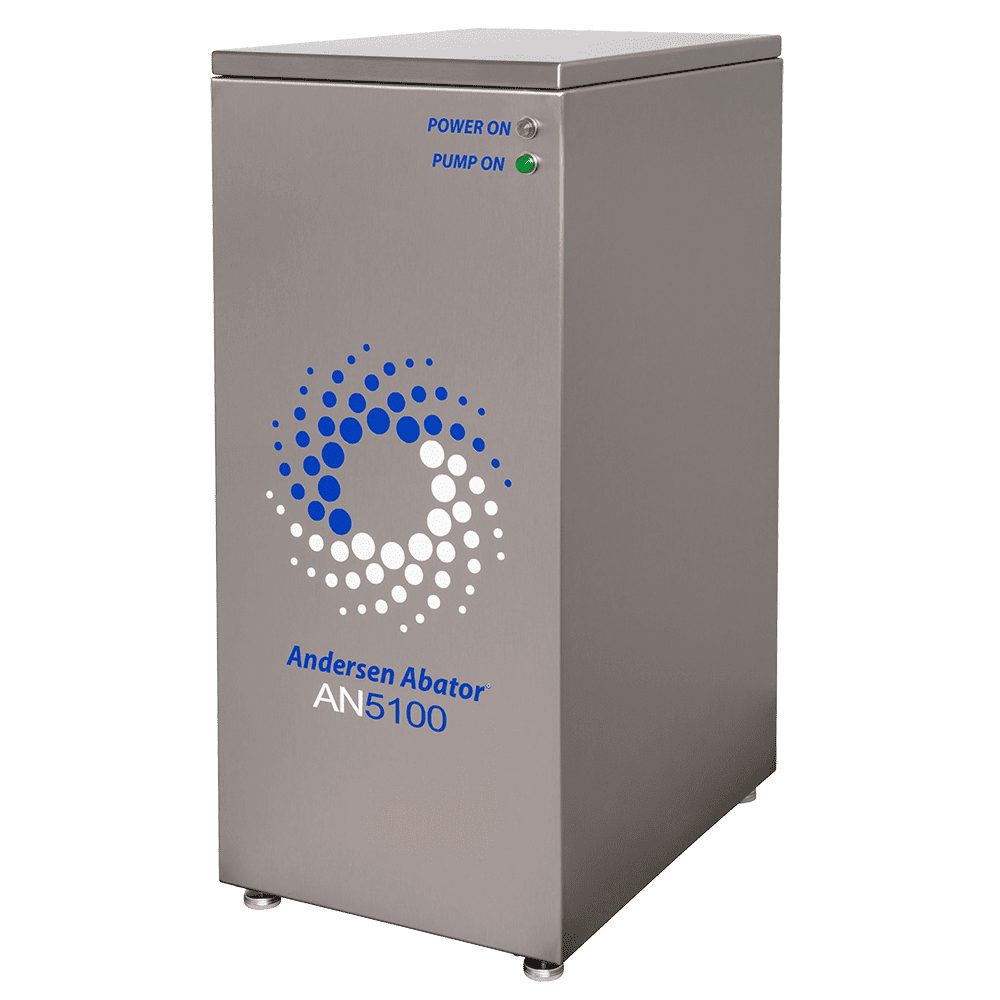
Andersen’s optional emissions abator is a simple, cartridge-based system that employs a dry catalyst resin. The resin converts ethylene oxide to biodegradable organic compounds. Replaceable cartridges are non-hazardous.
Smart Cabinet Design
A ventilation port in the back of the cabinet actively draws fresh air from the room through the cabinet and out the back exhaust through the entire cycle. This process ensures airflow in one direction and significantly mitigates risks.
Gentle
Achieve 10-6 SAL without those damaging downsides: high heat, steam, deep vacuum, oxidation or corrosion. Our process is damage-free.
Unmatched Compatibility
Sterilizes your most delicate instruments, electronics, drills, fiber optics, handpieces and cameras. As well as those plastic, fabric, cellulose or rubber items that you can’t sterilize with other methods. Most items except for food, drugs or liquids can be sterilized.
Right-sized
We have models from tabletop to refrigerator sized. Most designs fit conveniently on a countertop or table.
Active Aeration
Andersen’s purge probe flushes the sterilization bag with a constant flow of fresh air at the end of the cycle – no need to transfer items to a separate area. Active aeration continues indefinitely until products are removed.
Discover the key benefits of our advanced sterilization technology.
Affordable Solutions for Every Practice
Our units are economically priced, ensuring a quick return on investment.
User-Friendly Operation for All Staff
Set it and forget it – our system is incredibly easy to use.
Comprehensive Training for Your Team
We provide free training for your staff, ensuring effective operation.
Impact
Environmental Impact
Because we don’t sterilize “dead space” (see EO of Yesteryear tab), we can use a micro-dose of EO – The precise amount necessary to sterilize your items. This means our sterilizers use far less gas. As a consequence of using less, we are also naturally emitting far less.
We also offer optional emission abators. The simple, cartridge-based system employs a dry catalyst resin that converts ethylene oxide to biodegradable organic compounds. Replacement cartridges remove more than 99% of the EO in the exhaust stream, resulting in a fraction of a gram of total EO emissions throughout a multi-hour cycle. This tiny amount of EO is vented to the outside where it disperses rapidly, quickly becoming undetectable. Effectively making the process zero emission.
While traditional contract sterilization facilities can emit 1 or more tons of EO every year, even our worst-case calculation (running 24 hours a day, 365 a year, without stopping even for aeration), our systems emit 24 to 96.5 lbs. of EO per year. With an abator, those numbers become .24 to .97 lbs.

Two National-Level Regulatory Environmental Awards
Innovation is in our DNA. Recognized by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as an EO thought leader, Andersen was selected as one of eight international companies to collaborate on the development of strategies or technologies to reduce EO emissions to as close to zero as possible in its FDA Innovation Challenge. Challenge collaboration is ongoing.
In addition, Andersen was recognized with the 2020 Small Business Environmental Stewardship Award for its high-efficiency, low-emission sterilization process and its cooperation with State and Federal officials on regulatory and permitting issues.
2019 FDA Innovation Challenge 2 Winner
High-Efficiency EO Sterilization Process
2020 SBA Environmental Stewardship Award
Zero Emission Technology
Expert Guidance for Your Needs
Tell us a bit about your sterilization needs — our experts will guide you to the right EO solution.
